Nearly everyone on occasion experiences a throbbing headache that interferes with concentration at work or school, or saps the joy from the day.
But sometimes the source of that headache can be surprising. For many people, the pain that emanates from the head can be traced back to their teeth, their bite relationship and the alignment of the lower jaw.
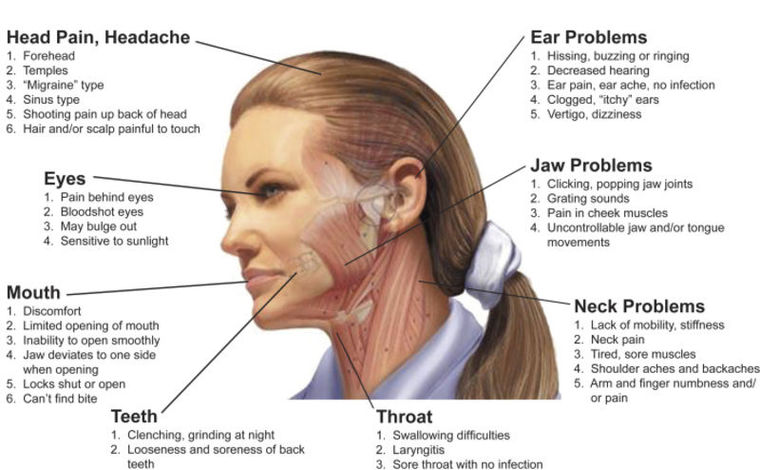
With many headaches, the cause could be the temporomandibular joint, or TMJ: the place at the front of the ear where the lower jaw and the temporal bone on the side of the head meet.
Sometimes the bite and the lower jaw are out of alignment, putting additional strain on muscles, which leads to the headaches. And for many, TMJ headaches aren’t going away because people try to mask the pain with medication rather than correct the underlying cause.
But how do you know a headache is caused by TMJ? Here are a few things to watch:
- Your bite feels off. The TMJ’s position is dictated by where our teeth come together in our bite. So if your bite feels off or your teeth don’t fit together well, there’s a good chance your TMJ joints are off, too.
- You have pain around your forehead, temples, back of head or radiating down your neck. Ninety percent of pain comes from muscle: if your muscles are not functioning well because of fatigue from supporting one or both of your TMJ joints in an improper position, they produce pain. It’s much like when you exercise or work hard and feel muscle pain later. The only difference is that TMJ is more subtle and chronic.
- You have forward head posture. Our heads are supposed to be centered over our shoulders. If yours is in front of your shoulders when you are upright, you have “forward head posture.” That relates to your bite and your airway. The human head weighs about eight to 10 pounds; the farther forward it is off the center axis, the more strain it places on neck muscles and vertebrae.
- You snore. Snoring is a red flag that respiration during sleep is disturbed, Abeles says. Several factors can lead to snoring, but one of the most important is the position of the lower jaw, he says. If your lower jaw is a little too far back, then the tongue is farther back as well.
If TMJ is the root of your migraine pain, we have treatment options available. Make sure you tell Dr. Clark about your discomfort during your next visit.
source: Dr. Fred Abeles, author of the book “Break Away: The New Method for Treating Chronic Headaches, Migraines and TMJ Without Medication” (www.FredAbeles.com)
 Nearly everyone on occasion experiences a throbbing headache that interferes with concentration at work or school, or saps the joy from the day.
But sometimes the source of that headache can be surprising. For many people, the pain that emanates from the head can be traced back to their teeth, their bite relationship and the alignment of the lower jaw.
With many headaches, the cause could be the temporomandibular joint, or TMJ: the place at the front of the ear where the lower jaw and the temporal bone on the side of the head meet.
Sometimes the bite and the lower jaw are out of alignment, putting additional strain on muscles, which leads to the headaches. And for many, TMJ headaches aren’t going away because people try to mask the pain with medication rather than correct the underlying cause.
But how do you know a headache is caused by TMJ? Here are a few things to watch:
Nearly everyone on occasion experiences a throbbing headache that interferes with concentration at work or school, or saps the joy from the day.
But sometimes the source of that headache can be surprising. For many people, the pain that emanates from the head can be traced back to their teeth, their bite relationship and the alignment of the lower jaw.
With many headaches, the cause could be the temporomandibular joint, or TMJ: the place at the front of the ear where the lower jaw and the temporal bone on the side of the head meet.
Sometimes the bite and the lower jaw are out of alignment, putting additional strain on muscles, which leads to the headaches. And for many, TMJ headaches aren’t going away because people try to mask the pain with medication rather than correct the underlying cause.
But how do you know a headache is caused by TMJ? Here are a few things to watch:
